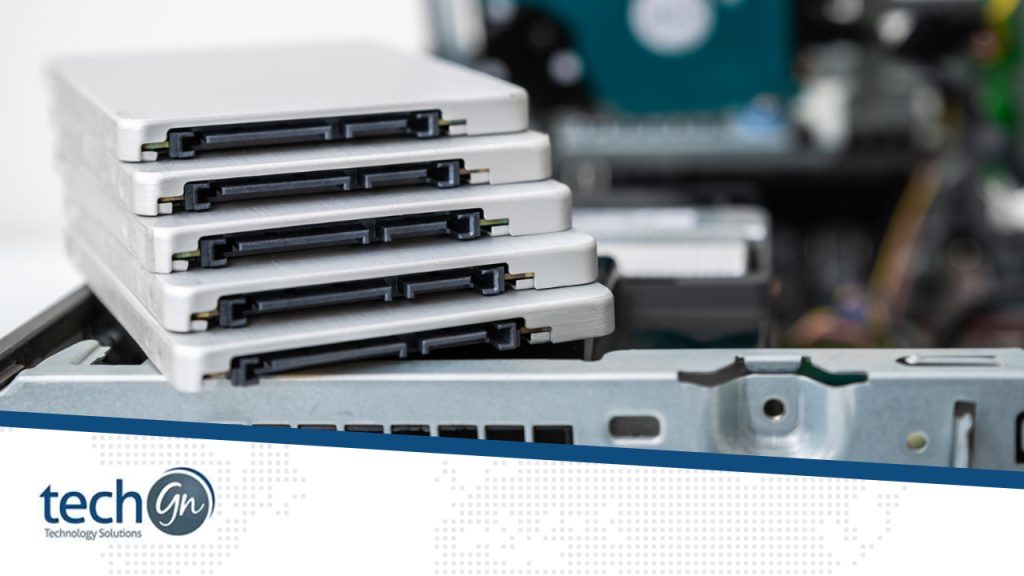
What are SSDs and HDDs?
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) have been the traditional storage solution for computers for decades. They store data on spinning disks, or platters, that are read and written by a moving magnetic head. This mechanical nature of HDDs affects their speed and durability.Solid-State Drives (SSDs)
Solid-State Drives (SSDs), on the other hand, use flash memory to store data. This technology is similar to what is used in USB flash drives, but SSDs are much faster and more reliable. Unlike HDDs, SSDs have no moving parts, which brings a host of advantages.Speed and Performance
One of the most significant benefits of SSDs over HDDs is speed. SSDs are incredibly fast, with data access times often measured in microseconds. This translates to faster boot times, quicker file transfers, and more responsive applications.
- Boot Time: An SSD can boot your computer in a matter of seconds, whereas an HDD might take significantly longer.
- File Transfers: SSDs can transfer large files in a fraction of the time it would take an HDD.
- Application Load Times: Programs and applications load much faster on an SSD, which enhances overall productivity.
Durability and Reliability
Since SSDs have no moving parts, they are more durable and reliable compared to HDDs. The mechanical components of an HDD are susceptible to wear and tear, which can lead to failures, especially if the drive is dropped or exposed to vibrations.
- Shock Resistance: SSDs can withstand shocks and vibrations better, making them ideal for laptops and mobile devices.
- Longevity: The lack of mechanical parts reduces the risk of physical damage and failure, contributing to a longer lifespan.
Power Efficiency
SSDs are more power-efficient than HDDs. The absence of spinning disks and moving heads means that SSDs consume less power, which can be a crucial factor for laptops and other battery-powered devices.
- Battery Life: Devices with SSDs typically have better battery life compared to those with HDDs.
- Heat Generation: SSDs generate less heat, contributing to a cooler and more efficient system operation.
Noise Levels
The mechanical nature of HDDs means they produce noise when in operation. The spinning platters and moving read/write heads can be quite audible, especially when the drive is working hard.
Silent Operation: SSDs operate silently, as they have no moving parts. This can make for a quieter and more pleasant user experience, particularly in quiet environments.
Size and Weight
SSDs are generally lighter and more compact than HDDs. This makes them an excellent choice for ultra-thin laptops and other compact devices where space and weight are critical considerations.
- Form Factor: SSDs come in various form factors, including the M.2 and NVMe drives, which are significantly smaller than traditional 2.5-inch HDDs.
- Portability: The reduced size and weight of SSDs enhance the portability of devices.
Cost Considerations
While SSDs have numerous advantages, cost can be a factor to consider. Historically, SSDs have been more expensive per gigabyte compared to HDDs. However, prices have been dropping steadily, making SSDs more affordable than ever.
- Cost per Gigabyte: HDDs still offer a lower cost per gigabyte, which can be beneficial for large storage needs on a budget.
- Value for Money: For performance and reliability, the investment in an SSD is often considered worth the extra cost.
Use Cases
Understanding the specific use cases for SSDs and HDDs can help in making the right choice.
- SSDs: Ideal for operating systems, software applications, gaming, and any tasks requiring fast access to data. Perfect for laptops and portable devices due to their durability and power efficiency.
- HDDs: Suitable for storing large amounts of data where speed is not as critical, such as backups, archives, and media libraries. They are also a cost-effective solution for desktop PCs requiring substantial storage capacity.
Bottom Line
Choosing between an SSD and an HDD depends on your specific needs and priorities. If speed, durability, and power efficiency are top priorities, an SSD is the clear winner. However, if you need a large amount of storage at a lower cost, an HDD might still be the better choice. As technology continues to advance, the gap between SSDs and HDDs in terms of price and storage capacity is narrowing. For many users, the benefits of SSDs—speed, reliability, and efficiency—make them an increasingly attractive option for both personal and professional use.Reviews
Tailoring Solutions